Introduction to Blockchain Technology
Blockchain is one of the most talked-about technologies today. Whether it’s cryptocurrency, supply chain systems, or digital identity, blockchain is making waves everywhere. But what actually makes it special? And how does it really work?
Let’s break it down in the simplest possible way—no technical jargon, just clear and easy-to-understand explanations.
Why Blockchain Matters Today

We live in a time where digital information can be copied, edited, or hacked. Blockchain stands out because it ensures trust and transparency without needing a middleman.
How Blockchain Is Reshaping Digital Systems
From banking to voting systems, blockchain is changing how information moves. It creates systems where you don’t have to “trust” anyone—the technology itself ensures security.
Understanding the Basics of Blockchain
What Is Blockchain?
Blockchain is a digital ledger—like a notebook—that records transactions. But instead of being stored in one place, it’s shared across thousands of computers.
Imagine a notebook that everyone can see, but no one can erase or change. That’s blockchain.
How It Differs from Traditional Databases
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Blockchain_final-086b5b7b9ef74ecf9f20fe627dba1e34.png)
Traditional databases are controlled by one authority. Blockchain isn’t. It’s decentralized, meaning no single person or organization owns it.
Key Elements of Blockchain
Blocks
A block stores information like transactions, timestamps, and a unique hash.
Chains
Blocks are linked together—each block references the previous one.
Nodes
Nodes are computers connected to the blockchain network that validate transactions.
Network
The entire system where all nodes interact, share, and update data.
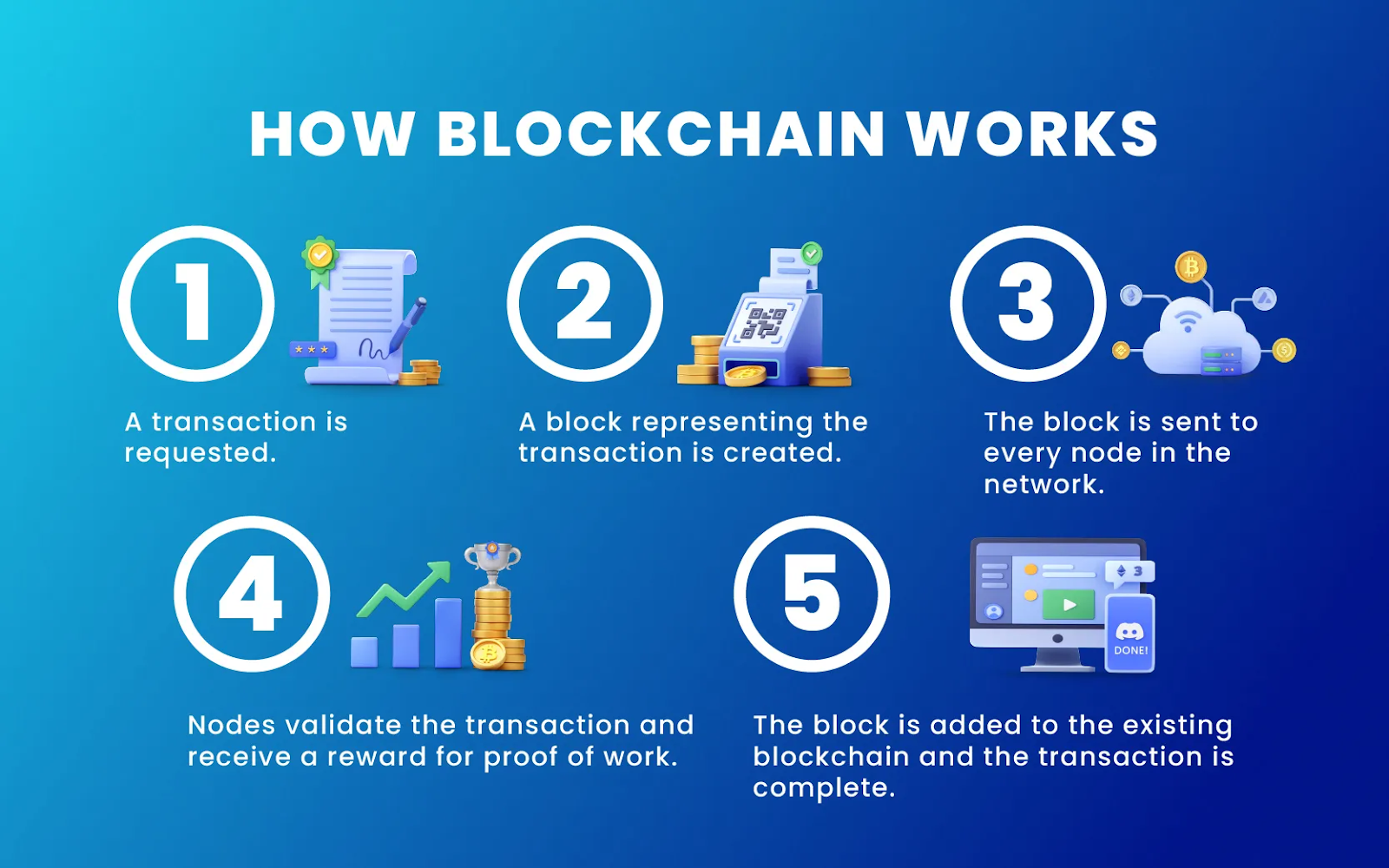
How Blockchain Works (Step-by-Step)
Step 1 – A Transaction Begins
Someone initiates a transaction, such as sending cryptocurrency or signing a digital document.
Step 2 – Transaction Broadcast to Network
The transaction is shared with all computers (nodes) on the blockchain.
Step 3 – Verification by Nodes
Nodes verify if the transaction is valid. They check:
- Wallet signatures
- Funds availability
- Data accuracy
Step 4 – Creating a New Block
Once verified, the transaction joins others in a new block.
Step 5 – Adding the Block to the Chain
After validation, the new block is added to the blockchain, becoming permanent and unchangeable.
Types of Blockchain

Public Blockchains
Open to everyone. Examples: Bitcoin, Ethereum.
Private Blockchains
Owned and controlled by organizations. Only authorized users can join.
Consortium Blockchains
Managed by a group of organizations working together.
Hybrid Models
A mix of public and private blockchain features.
Core Features of Blockchain Technology
Decentralization
Data is not stored in one central place—it’s distributed globally.
Transparency
Everyone can view the transactions, increasing trust.
Immutability
Data cannot be changed once added to the blockchain.
Security
Cryptographic techniques protect the entire network.
Blockchain Consensus Mechanisms
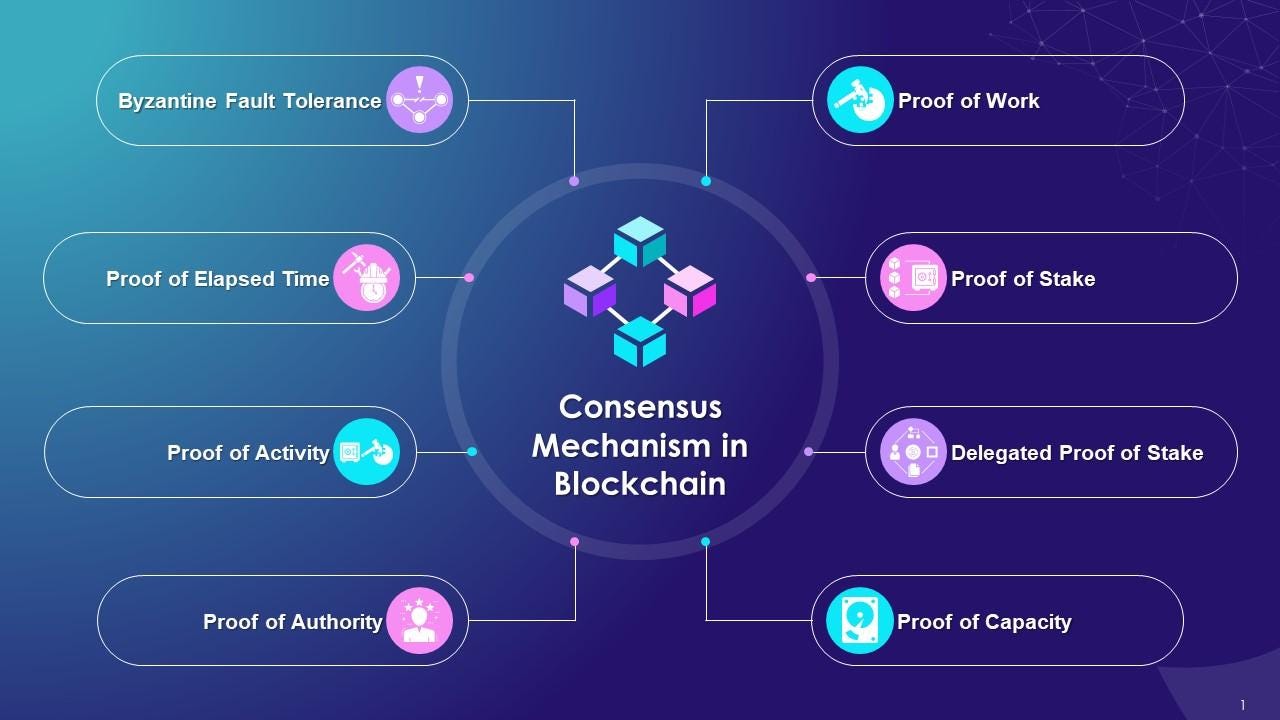
Proof of Work (PoW)
Uses computing power to verify transactions (e.g., Bitcoin mining).
Proof of Stake (PoS)
Validators stake coins instead of using energy-heavy hardware.
Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS)
Users vote for validators who secure the network.
Other Emerging Consensus Models
Includes Proof of Authority, Proof of History, and more.
Real-World Uses of Blockchain
Cryptocurrencies
Bitcoin, Ethereum, and thousands of others run on blockchain.
Supply Chain Tracking
Helps track goods from manufacturer to customer.
Digital Identity
Allows individuals to control their own identity documents.
Smart Contracts
Digital agreements that execute automatically without middlemen.
Why Blockchain Is Considered Secure
Hashing
Transforms data into a unique digital fingerprint.
Encryption
Protects sensitive information from hackers.
Distributed Ledger Technology
The system is shared across thousands of computers—nearly impossible to hack.
Limitations of Blockchain
Scalability Challenges
Some blockchains struggle to process thousands of transactions per second.
Energy Consumption
Proof-of-work blockchains require massive electricity.
Regulation Issues
Governments are still figuring out how to regulate blockchain.
The Future of Blockchain

Web3 and Decentralized Apps
Apps that run without central servers are rising fast.
Enterprise-Level Adoption
More businesses are integrating blockchain into their operations.
AI and Blockchain Integration
AI + Blockchain = secure, intelligent, automated systems.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology isn’t just a trend—it’s a powerful system that is transforming industries worldwide. By making information transparent, secure, and decentralized, blockchain creates a world where trust comes from technology, not people. Understanding how blockchain works gives you a massive advantage in today’s digital era.
FAQs
1. Is blockchain the same as Bitcoin?
No. Bitcoin uses blockchain, but blockchain is a technology that powers many applications.
2. Can blockchain be hacked?
It’s extremely difficult due to decentralization and encryption.
3. Do I need coding skills to understand blockchain?
Not at all. Its basic concept is easy and logical.
4. What industries use blockchain?
Finance, healthcare, logistics, voting systems, and more.
5. Is blockchain the future of the internet?
Many experts believe blockchain will power the next wave of internet technology (Web3).